.png)
Your guide to
Bearing relubrication
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the crucial topic of bearing relubrication. Did you know that faulty bearings are the leading cause of motor failures? To ensure the longevity and reliability of your electric motors, it's imperative to include regular bearing lubrication in your maintenance routine. Monitoring lubricant levels is a simple yet effective way to detect leaks and contamination before they harm your motor.
3 Factors to Consider
When it comes to bearing relubrication, there are three key factors to consider: the correct relubrication interval, the appropriate lubricant type, and the suitable lubricant grade. Typically, these factors are determined based on the motor's lubrication plan and the manufacturer's recommendations.
If you're uncertain, our dedicated repair team at IMS is always ready to assist you in sourcing the necessary supplies. Moreover, this guide is a valuable resource even when manufacturer recommendations are unavailable. It equips you with the knowledge and best practices for ensuring your electric motors run optimally.
The Importance of Bearing Relubrication
Did you know? Faulty bearings are the number one cause for motor failures. You can extend the life and reliability of your electric motors by adding one step to your routine maintenance strategy: regularly monitor bearing lubricant levels. By monitoring these levels, you may catch leaks and contamination before it’s damaging to the motor.
You should determine the following information:
-
The correct relubrication interval
-
The lubricant type
-
The lubricant grade
This information is typically based on the motor’s lubrication plant and the manufacturer’s recommendations. However, the repair team at IMS can always help you source the supplies you need for this process.
You can also follow the guidance provided here when the manufacturer recommendation is not available.
The Function of Lubricants
You should know the critical tasks that bearing lubricants perform. Some tasks include:
-
Separating rolling or sliding surfaces
-
Reducing wear
-
Minimizing the coefficient of friction (example: reducing heat)
-
Removing heat generated by friction
-
Blocking the ingress of contamination
-
Preventing corrosion
Grease-lubricated Bearings
For grease-lubricated bearings that aren't "sealed for life," regular relubrication through grease fittings is essential. Choosing the right grease involves considering compatibility, quantity, and relubrication intervals.
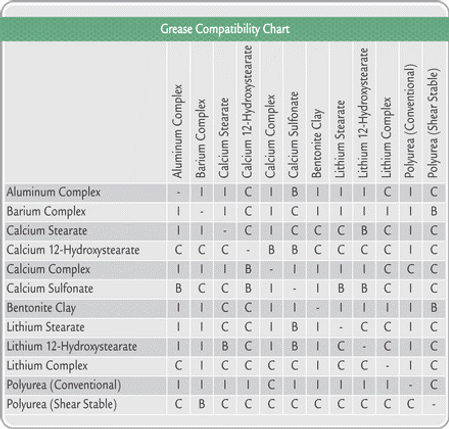
Grease Incompatibility
Grease incompatibility can lead to issues ranging from increased bearing wear to catastrophic machine failure. Always exercise caution, and when in doubt, consult both manufacturers.
Signs of Lubricant or Additive Incompatibility
-
Unusual increases in heat generation
-
Metal wear
-
Vibration or noise emission
-
Unusual color shifts in the lubricant
-
A sudden increase in foreign particles
-
Leaks due to viscosity changes
-
Foaming
-
Formation of emulsions
-
Appearance of fluid separation or gels in sight glasses
Before inserting grease, ensure the grease fitting is clean and the drain plug is removed. After relubrication, run the motor for at least 30 minutes with the drain plug out to purge excess grease.
Grease Quantity: Avoid Over-filling
Over-filling with grease can lead to problems such as grease shear and motor insulation system contamination, potentially causing winding failure.
Use the following equation to estimate the appropriate grease quantity:
G = 0.11 x OD x W (English Units)
G = 0.0048 x OD x W (Metric Units)
Where:
-
G = Quantity of Grease (fluid oz. or mm)
-
OD = Bearing OD (inches or mm)
-
W = Width of Bearings (inches or mm)
Grease Lubrication Intervals
For Normal Operating Conditions
Grease relubrication intervals for normal operating conditions are a function of two variables:
-
Bearing speed
-
Bore size
Using the chart provided below, determine the relubrication level as follows:
-
Find the motor’s RPM on the horizontal axis
-
Draw a vertical line from the motor’s RPM to the curve that represents the bearing’s inside diameter (mm) or the next smallest dimension.
-
From that point, draw a horizontal line to intersect the hours of operation (re-lubrication interval) for the applicable bearing type.
For Abnormal Operating Conditions
What constitutes abnormal operating conditions?
-
High temperature
-
Vibration
-
Contaminants
If the operating conditions are abnormal, more frequent relubrication may be required. Other than experience, there isn’t a simple rule for increasing the relubrication frequency for such conditions.
Oil-Lubricated Bearings
For oil-lubricated bearings, use the following criteria to select:
-
Compatible oil
-
Viscosity
-
Relubrication interval
Oil Compatibility
Fun fact: Oil suppliers use a variety of additivities, which makes some incompatible. The same problems that arise with grease incompatibility, can occur with oil compatibility. The same precautions mentioned for grease, should be followed for oil. Don’t mix oils if there’s any hint of uncertainty.
Oil Viscosity for Rolling Element Bearings
The chart below provides guidelines for selecting the correct oil viscosity for rolling element bearings in horizontal motors based on:
-
Bearing Operating Temperature (°C or °F)
-
Bearing Pitch Diameter (dm=(ID+OD)/2) in mm
-
Operating Speed (n) in rpm
-
Bearing load level (light/normal) or (heavy/impact)
Example
To determine the correct oil viscosity for a 6210 ball bearing operating at 3600 RPM at 90°C (194°F) under normal loading conditions (the ratio of the bearing’s dynamic capacity to the applied load (Cr/Pr < 0.12):
Calculate the bearing pitch diameter:
(ID + OD/2) = dm (in mm)
(50+90)/2 = 70 mm
Determine the dmn value by multiplying the bearing pitch diameter by the operating speed:
Dm(mm) x n (rpm) = dmn
Next, we use the table to select the appropriate viscosity. In this case, we would choose ISO VG 56 or VG 68 or turbine oil.
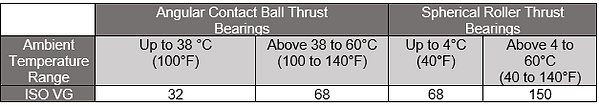
Selecting Oil Viscosity for Vertical Motors
For vertical motors, use this table for selecting the correct oil viscosity, regardless of bearing size & speed.
Important: If the motor lubrication plate specifies synthetic oil, do not substitute another oil.
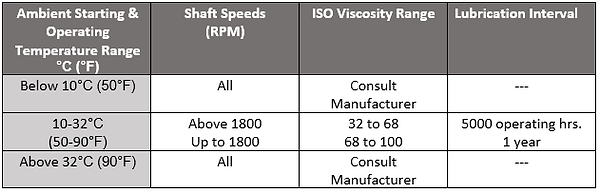
Selecting Oil Viscosity & Lubrication Intervals for Sleeve Bearing Motors
Knowledge Check: The clearance between what two parts is critical with sleeve bearings?
Answer: Between the shaft journal and the bearing bore
How Lubrication in Sleeve Bearings Prevents Catastrophic Failure
Short-term, metal-to-metal contact increases the bearing temperature which is known as wiping. Wiping degrades the baring itself and can cause failure in your motor. In order to maintain sleeve bearing clearances, you should follow the lubrication guidelines here:
When is more frequent oil changes required (rather than the recommendations above)?
Severe service conditions such as:
-
Frequent starting & stopping
-
Damp or dusty environments
-
Extreme temperatures
Summary
In summary, proper bearing relubrication is essential for maintaining motor performance and extending its lifespan. The choice of lubricant, its compatibility, and the relubrication intervals play critical roles in this process. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your electric motors operate at their best under various conditions, ultimately saving you time and money.


Contact
24/7 Emergency Service
Contact us with any comments, questions or concerns!
(864) 226-2893